Hisashi Ouchi: The Tragedy And Legacy Of Radiation Exposure
Who was Hisashi Ouchi?
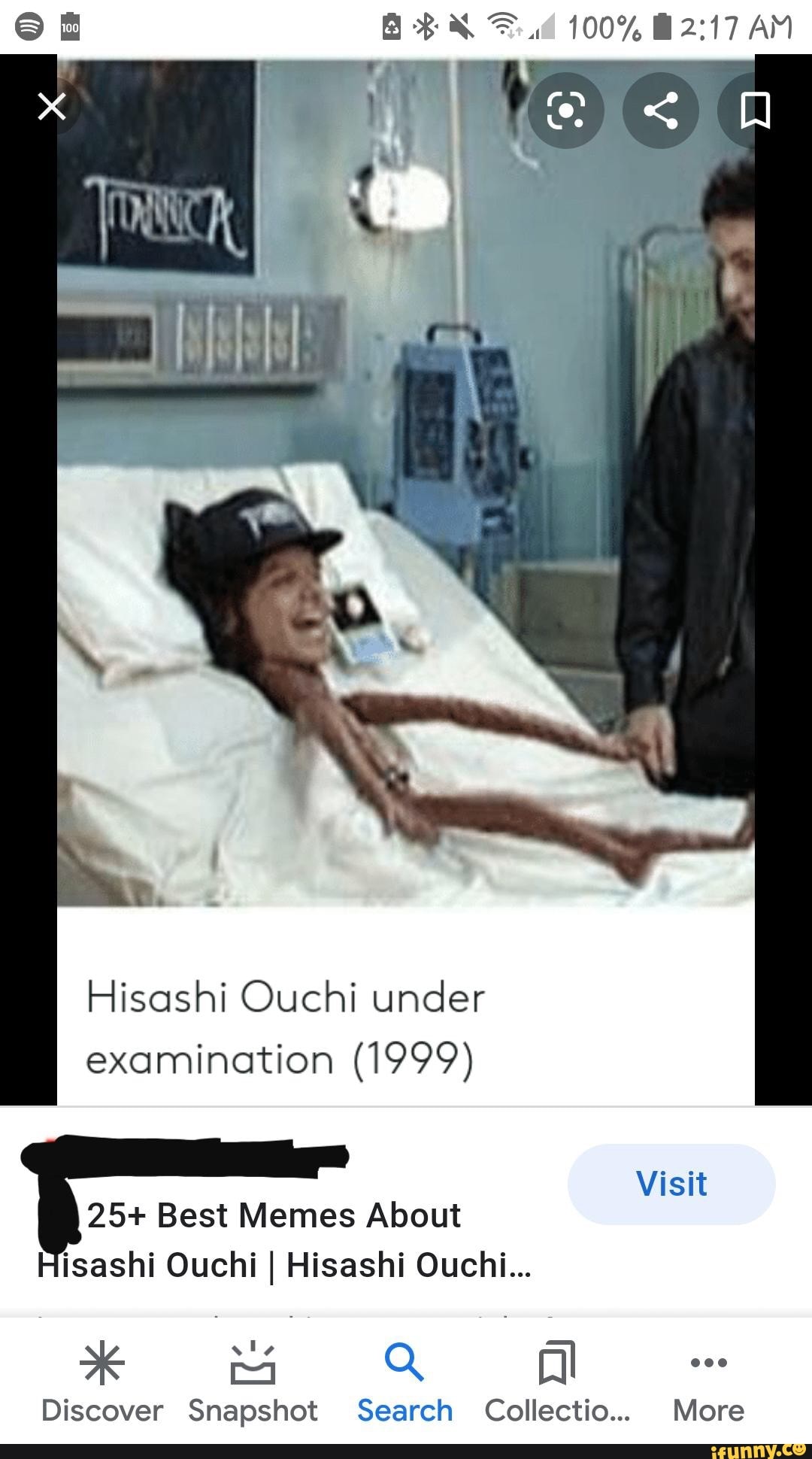
Hisashi Ouchi was a Japanese nuclear technician who suffered a criticality accident at the JCO Tokaimura plant in 1999. During the accident, Ouchi was exposed to an extremely high dose of radiation, estimated to be around 17 sieverts. This is equivalent to the amount of radiation a person would receive from 1700 chest X-rays.
Ouchi's case was one of the most severe and prolonged cases of radiation poisoning ever recorded. He underwent extensive medical treatment, including multiple surgeries and skin grafts, but his condition continued to deteriorate. He died three months after the accident from multiple organ failure.
- The Legendary Drummer Randy Castillo A Musical Master
- Sabrina Carpenters Height And Weight A Comprehensive Guide
Ouchi's case highlighted the dangers of radiation exposure and the need for strict safety protocols in nuclear facilities. It also led to a number of changes in the way radiation accidents are treated, including the development of new medical protocols and the establishment of international guidelines for radiation protection.
hisashi ouchiIntroduction
Radiation ExposureIntroduction
Medical TreatmentIntroduction
Hisashi Ouchi
Hisashi Ouchi's case highlighted the dangers of radiation exposure and the need for strict safety protocols in nuclear facilities.
- Radiation exposure
- Medical treatment
- Nuclear safety
- Radiation protection
- Emergency response
- Public health
- Media coverage
- Ethical considerations
Ouchi's case was one of the most severe and prolonged cases of radiation poisoning ever recorded. He underwent extensive medical treatment, including multiple surgeries and skin grafts, but his condition continued to deteriorate. He died three months after the accident from multiple organ failure.
- Legendary Guitarist Jimmy Pages Impact On Rock Music
- How Old Was Justin Chambers In The First Season Of Greys Anatomy
Radiation exposure
Radiation exposure is a major component of the story of Hisashi Ouchi, a Japanese nuclear technician who suffered a criticality accident at the JCO Tokaimura plant in 1999. Ouchi was exposed to an extremely high dose of radiation, estimated to be around 17 sieverts, which is equivalent to the amount of radiation a person would receive from 1700 chest X-rays.
Ouchi's case highlighted the dangers of radiation exposure and the need for strict safety protocols in nuclear facilities. It also led to a number of changes in the way radiation accidents are treated, including the development of new medical protocols and the establishment of international guidelines for radiation protection.
The connection between radiation exposure and Hisashi Ouchi is a reminder of the importance of nuclear safety and the need for continued research into the effects of radiation on the human body.
Medical treatment
Hisashi Ouchi's case highlighted the challenges and limitations of medical treatment in the face of severe radiation exposure.
- Emergency response
The immediate medical response to Ouchi's accident was critical in stabilizing his condition and preventing further deterioration. He was rushed to the University of Tokyo Hospital, where he received specialized treatment for radiation exposure.
- Skin grafts
Ouchi's skin was severely damaged by the radiation exposure, and he underwent multiple skin grafts in an attempt to repair the damage. However, the grafts were not successful, and his skin continued to deteriorate.
- Organ failure
The radiation exposure also caused damage to Ouchi's internal organs, leading to multiple organ failure. He underwent several surgeries to try to repair the damage, but his condition continued to worsen.
- Palliative care
In the final stages of his illness, Ouchi received palliative care to manage his pain and symptoms. He died three months after the accident from multiple organ failure.
Ouchi's case demonstrated the need for continued research into the medical treatment of radiation exposure victims. It also highlighted the importance of developing new and more effective treatments for radiation-induced injuries.
Nuclear safety
Hisashi Ouchi's case highlighted the critical importance of nuclear safety in preventing and mitigating the consequences of radiation accidents.
Nuclear safety encompasses a wide range of measures and practices designed to prevent or minimize the release of radioactive materials from nuclear facilities. These measures include:
- Proper design and construction of nuclear facilities
- Rigorous operating procedures
- Regular maintenance and inspections
- Emergency preparedness and response plans
Ouchi's accident occurred at the JCO Tokaimura plant in Japan, which was a uranium reprocessing facility. The accident was caused by a criticality excursion, which is a sudden and uncontrolled release of nuclear energy. The criticality excursion occurred when a worker added too much uranium to a precipitation tank, causing the tank to become supercritical.
The accident resulted in the release of a large amount of radiation, which exposed workers in the facility, including Ouchi. Ouchi received a lethal dose of radiation and died three months later from multiple organ failure.
Ouchi's case is a reminder of the importance of nuclear safety in preventing and mitigating the consequences of radiation accidents. Nuclear facilities must be designed, constructed, and operated in a way that minimizes the risk of accidents. Emergency preparedness and response plans must be in place to ensure that workers and the public are protected in the event of an accident.
Radiation protection
Radiation protection is a critical component of nuclear safety and is essential for preventing and mitigating the consequences of radiation accidents. Hisashi Ouchi's case highlights the importance of radiation protection in the nuclear industry and the need for strict adherence to safety protocols.
Ouchi was a Japanese nuclear technician who was involved in a criticality accident at the JCO Tokaimura plant in 1999. The accident occurred when a worker added too much uranium to a precipitation tank, causing the tank to become supercritical and release a large amount of radiation. Ouchi was exposed to a lethal dose of radiation and died three months later from multiple organ failure.
Ouchi's case demonstrated the importance of radiation protection in preventing and mitigating the consequences of radiation accidents. The accident could have been prevented if the worker had followed proper safety procedures and if the facility had been equipped with adequate radiation protection measures.
Radiation protection is a complex and challenging field, but it is essential for ensuring the safety of workers and the public in the nuclear industry. By understanding the risks of radiation exposure and by implementing effective radiation protection measures, we can prevent accidents like the one that happened to Hisashi Ouchi.
Emergency response
Emergency response played a crucial role in the case of Hisashi Ouchi, a Japanese nuclear technician who suffered a criticality accident at the JCO Tokaimura plant in 1999. Ouchi was exposed to an extremely high dose of radiation, estimated to be around 17 sieverts, which is equivalent to the amount of radiation a person would receive from 1700 chest X-rays.
Ouchi's case highlighted the importance of a swift and coordinated emergency response in the event of a radiation accident. The immediate medical attention he received helped to stabilize his condition and prevent further deterioration. He was rushed to the University of Tokyo Hospital, where he received specialized treatment for radiation exposure.
The emergency response also included measures to contain the spread of radiation and protect other workers and the public. The JCO Tokaimura plant was evacuated, and a 10-kilometer radius around the plant was designated as a restricted zone. Radiation monitoring and decontamination efforts were also carried out to minimize the risk of further exposure.
The emergency response to the Hisashi Ouchi accident demonstrated the importance of preparedness and coordination in managing radiation accidents.
Public health
Hisashi Ouchi's case highlighted the importance of public health in preventing and mitigating the consequences of radiation accidents.
- Radiation exposure and its effects
Radiation exposure can have a wide range of effects on human health, depending on the dose and type of radiation. Ouchi's case demonstrated the severe and life-threatening effects of high-dose radiation exposure, including skin damage, organ failure, and death.
- Emergency preparedness and response
Public health agencies play a critical role in preparing for and responding to radiation accidents. This includes developing and implementing emergency plans, training first responders, and providing public information about radiation risks and protective measures.
- Long-term health effects
Radiation exposure can also have long-term health effects, including an increased risk of cancer and other diseases. Public health agencies work to monitor and track the health of populations exposed to radiation and to provide support and care for those affected.
- Public communication and education
Public health agencies play an important role in communicating with the public about radiation risks and protective measures. This includes providing accurate and timely information about radiation hazards, and educating the public on how to stay safe in the event of a radiation accident.
Ouchi's case is a reminder of the importance of public health in protecting the health of the population from the risks of radiation exposure. Public health agencies play a vital role in preparing for, responding to, and mitigating the consequences of radiation accidents.
Media coverage
The media coverage of Hisashi Ouchi's case played a significant role in raising public awareness about the dangers of radiation exposure and the importance of nuclear safety. The extensive media coverage of Ouchi's suffering and eventual death helped to humanize the issue of radiation exposure and to make the public more receptive to calls for stricter safety measures at nuclear facilities.
The media also played a role in holding the Japanese government and the nuclear industry accountable for the accident. The relentless media coverage of Ouchi's case helped to keep the accident in the public eye and to put pressure on the authorities to take action to prevent similar accidents in the future.
The media coverage of Hisashi Ouchi's case is a reminder of the important role that the media can play in raising public awareness about important issues and in holding those in power accountable.
Ethical considerations
The case of Hisashi Ouchi, a Japanese nuclear technician who suffered a criticality accident in 1999, raises a number of ethical considerations. Ouchi was exposed to an extremely high dose of radiation, estimated to be around 17 sieverts, which is equivalent to the amount of radiation a person would receive from 1700 chest X-rays. He underwent extensive medical treatment, including multiple surgeries and skin grafts, but his condition continued to deteriorate. He died three months after the accident from multiple organ failure.
One of the ethical considerations raised by Ouchi's case is the question of whether it is ethical to continue treating a patient who has no chance of survival. Ouchi's doctors knew that he would not survive, but they continued to treat him in order to relieve his suffering and to learn more about the effects of radiation exposure. Some people argue that it is ethical to continue treating a patient even if there is no chance of survival, because it is important to relieve the patient's suffering and to learn more about the disease. Others argue that it is unethical to continue treating a patient who has no chance of survival, because it is a waste of resources and it can prolong the patient's suffering.
Another ethical consideration raised by Ouchi's case is the question of whether it is ethical to use experimental treatments on a patient who has no other options. Ouchi's doctors used a number of experimental treatments in an attempt to save his life. Some people argue that it is ethical to use experimental treatments on a patient who has no other options, because it gives the patient a chance to survive. Others argue that it is unethical to use experimental treatments on a patient who has no other options, because it is risky and it can cause the patient more suffering.
The ethical considerations raised by Ouchi's case are complex and there are no easy answers. It is important to weigh the benefits and risks of each treatment option and to make a decision that is in the best interests of the patient.
Frequently Asked Questions about Hisashi Ouchi
This section provides answers to commonly asked questions about Hisashi Ouchi, a Japanese nuclear technician who suffered a criticality accident in 1999.
Question 1: What happened to Hisashi Ouchi?
Hisashi Ouchi was a nuclear technician who was involved in a criticality accident at the JCO Tokaimura plant in Japan in 1999. A criticality accident is a sudden and uncontrolled release of nuclear energy. Ouchi was exposed to a lethal dose of radiation during the accident and died three months later from multiple organ failure.
Question 2: What were the long-term effects of the radiation exposure on Hisashi Ouchi?
The radiation exposure had a devastating impact on Ouchi's body. He suffered from severe skin damage, organ failure, and a compromised immune system. Despite undergoing multiple surgeries and skin grafts, his condition continued to deteriorate until his death three months after the accident.
Question 3: What lessons were learned from the Hisashi Ouchi accident?
Ouchi's case highlighted the importance of nuclear safety and the need for strict adherence to safety protocols. It also led to improvements in the medical treatment of radiation exposure victims and the development of new radiation protection measures.
Question 4: What is the legacy of Hisashi Ouchi?
Hisashi Ouchi's case serves as a reminder of the dangers of radiation exposure and the importance of nuclear safety. His story has been told in books, articles, and documentaries, and his name has become synonymous with the devastating effects of radiation exposure.
Summary: Hisashi Ouchi's case is a tragic reminder of the dangers of radiation exposure and the importance of nuclear safety. His story has helped to raise awareness about the risks of radiation and has led to improvements in the medical treatment of radiation exposure victims.
Conclusion
Hisashi Ouchi's case is a stark reminder of the devastating effects of radiation exposure and the importance of nuclear safety. His story has helped to raise awareness about the risks of radiation and has led to improvements in the medical treatment of radiation exposure victims.
Ouchi's case also highlights the need for continued research into the effects of radiation on the human body. By understanding the risks of radiation exposure and by developing effective radiation protection measures, we can prevent accidents like the one that happened to Hisashi Ouchi from happening again.
Article Recommendations
- Coleturgis Thrilling Life Below Zero A Biography Of Resilience
- Gabriel Machts Stature Unraveling The Actors Height


Detail Author:
- Name : Deven Dibbert
- Username : craig16
- Email : robert.weimann@yahoo.com
- Birthdate : 1980-09-16
- Address : 8234 Hilda Neck West Tyshawn, IN 45595-3743
- Phone : 1-878-310-6427
- Company : Littel and Sons
- Job : Child Care
- Bio : Nulla quo quo molestiae mollitia et. Et dolores ipsum expedita. Tempore et a magni totam numquam ut id. Ut impedit deserunt qui praesentium et iure ut.
Socials
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@vivianne8505
- username : vivianne8505
- bio : Quaerat earum et dolor quam vel distinctio. Dolor eum odio iusto sunt.
- followers : 3103
- following : 1185
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/vivianne_sanford
- username : vivianne_sanford
- bio : Laboriosam dolor molestias ipsa suscipit quaerat.
- followers : 2151
- following : 93